
What's New in Mechanical at 2019 R3?
Play a video describing the new features:
Click any topic below for more information:
|
Analysis Enhancements Topology Optimization External Model |
Fracture Geometry and Connections Mesh Materials Usability and Interface |
Additive Manufacturing Results and Post Processing Aqwa |
|
Helpful Links These are for your convenience. They require internet access and will open in a new browser window. Some also require Customer Portal login credentials. |
|
"What's New" for Other Mechanical Releases Use these to easily see the "What's New" pages for other releases of Mechanical. Use these same links to return to this "What's New" page.
|
Coupled Field System (Thermal Structural)
Mechanical now offers two new analysis types: Coupled Field Static and Coupled Field Transient. These analyses enable you to perform either a static or transient simulation between interacting structural and thermal physics. You can perform either a Strong Coupling at the matrices level or Weak Coupling where additional coupling terms are added at the load vector level. These analyses support the common structural and thermal environmental options in addition to the features and options that are specific to the analyses.
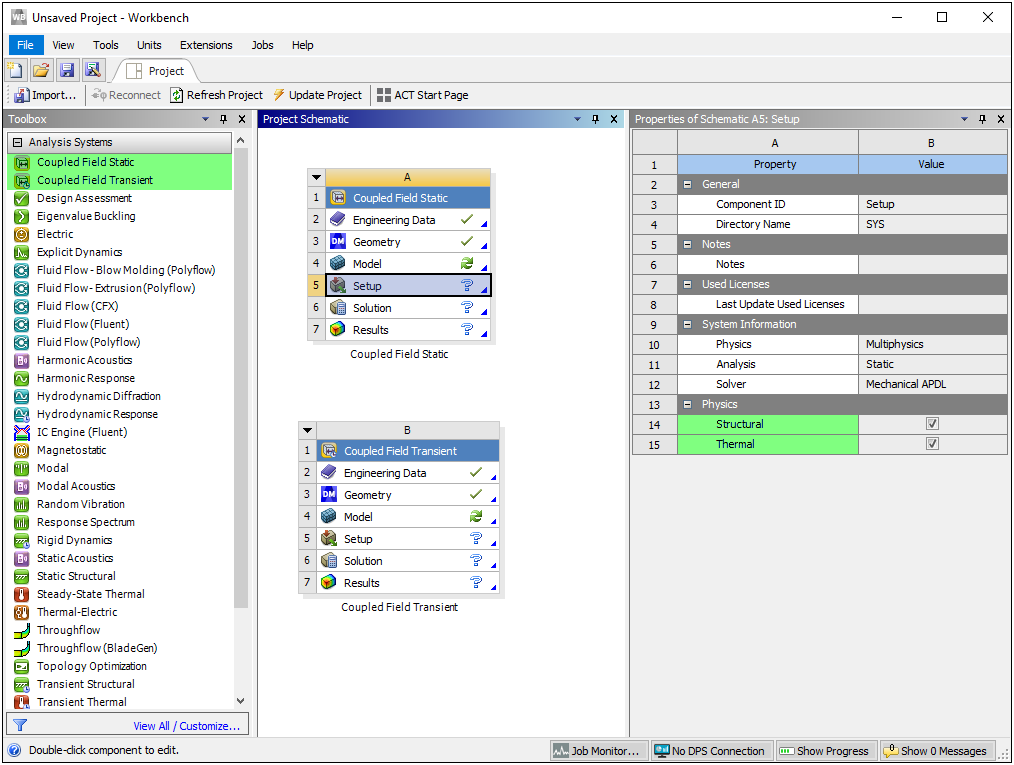
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
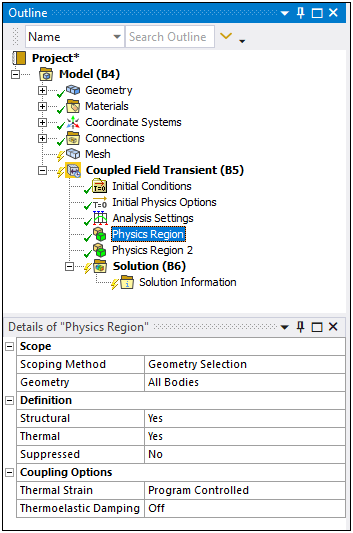
You use the Physics Region object to specify a body or bodies as either Structural or Thermal physics type, or both. As illustrated below, the application supports interaction between bodies that have coupled fields specified with other bodies of the model that have only structural or thermal physics specified.
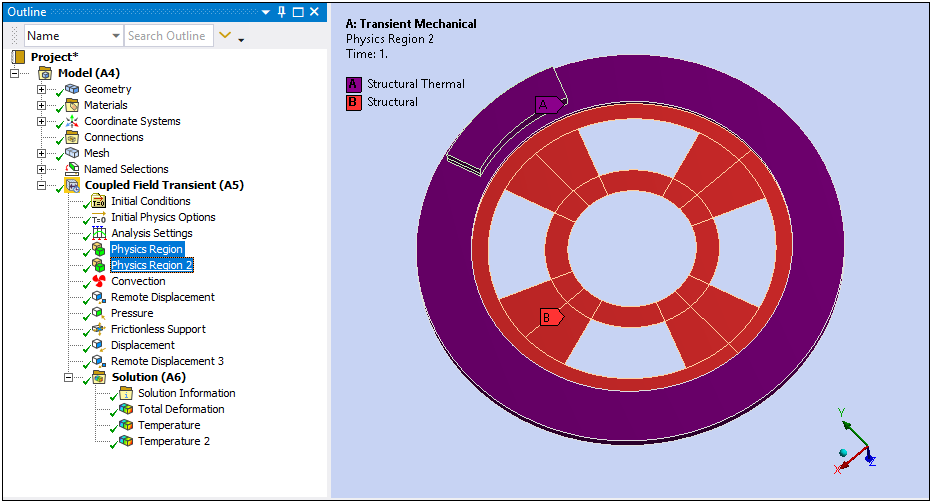
When both Structural and Thermal physics are enabled using the Physics Region object, the Thermal Strain coupling can be specified as either Strong (Program Controlled) or Weak coupling and to include the coupling effect of Thermoelastic Damping (Coupled Field Transient only). The coupling effect is also provided through the new boundary conditions: Plastic Heating and Viscoelastic Heating.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
Inverse Solving for Static Structural Analysis
Now, for a Static Structural nonlinear analysis with the Large Deflection property set to On, you can perform an inverse solving on a known input geometry that is already deformed under a set of loads that produced the deformation. This is done using the new Advanced Analysis Settings property, Inverse Option. Furthermore, during the same analysis, you can incorporate forward solving steps following the inverse steps with the additional sets of loads and boundary conditions.
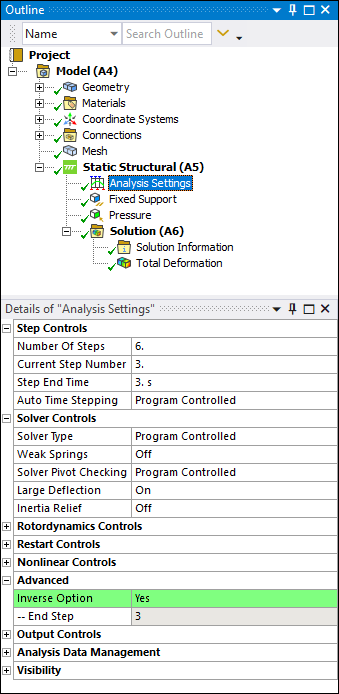
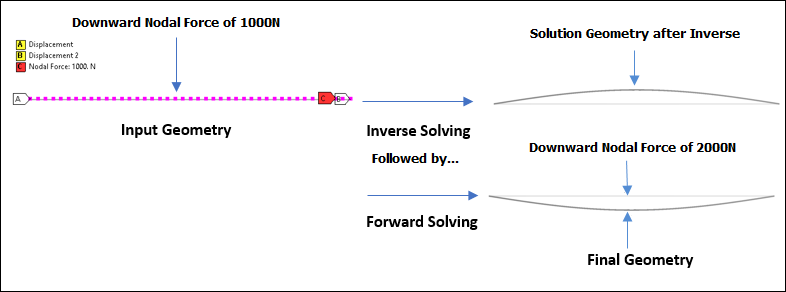
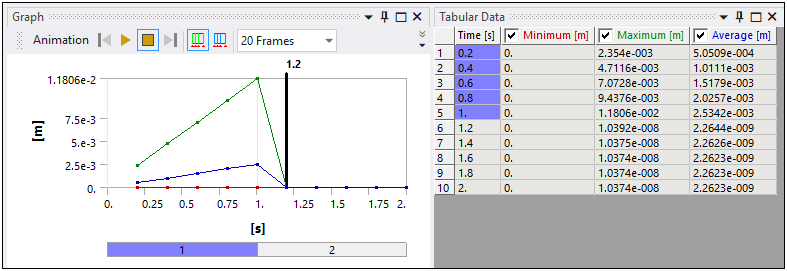
The results created during the solution using the Inverse Option are shown with a colored highlight in the Graph and Tabular Data window. And you can save the solution/reference geometry using the context (right-click) menu option Insert > Export > STL on a deformation result.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
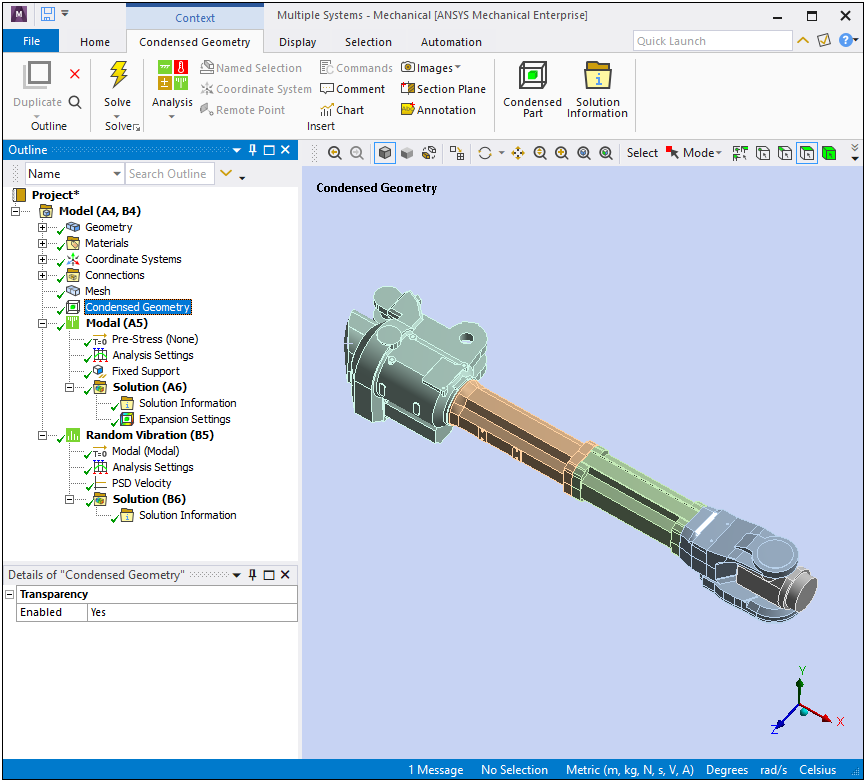
Substructuring with Random Vibration Analysis
The substructuring feature to create Condensed Parts now supports the Random Vibration analysis.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
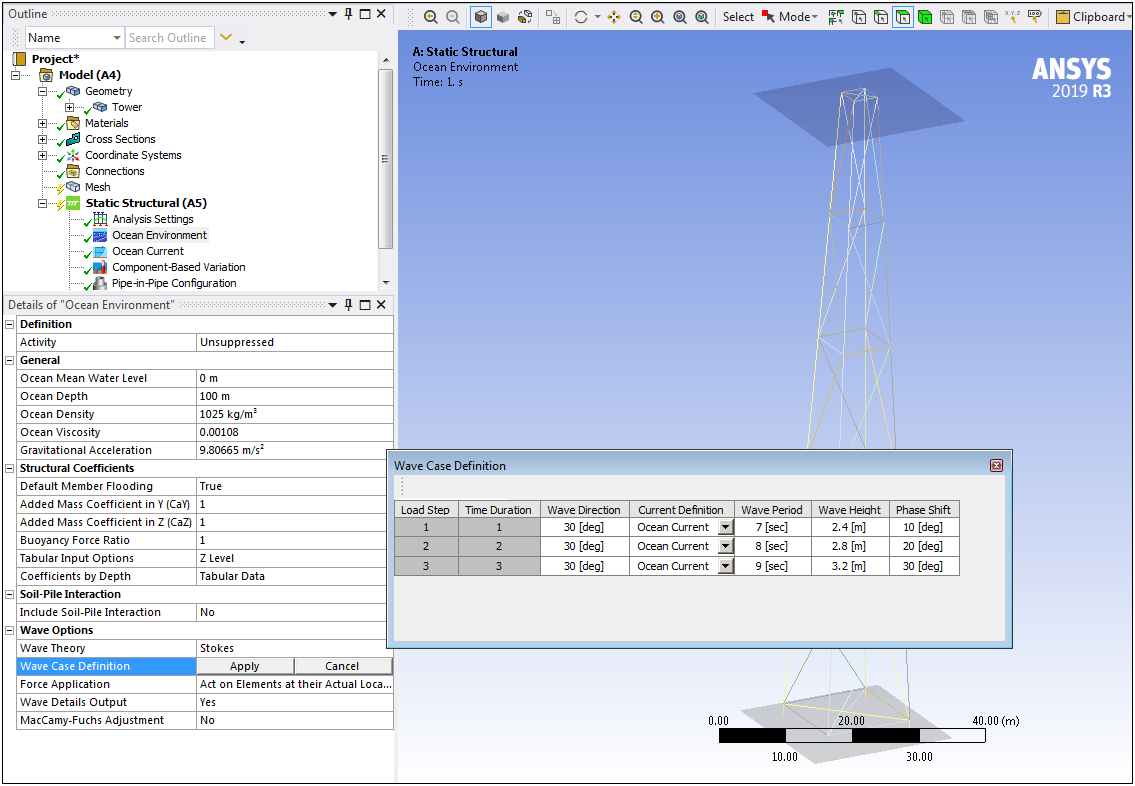
Offshore ACT Extension
The new Offshore ACT Extension exposes the MAPDL Ocean functionality in Workbench. This enables you to calculate submerged beam loads for various sea states. Mechanical supports this extension for the Static Structural, Transient Structural, Modal, and Harmonic Response analysis systems.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
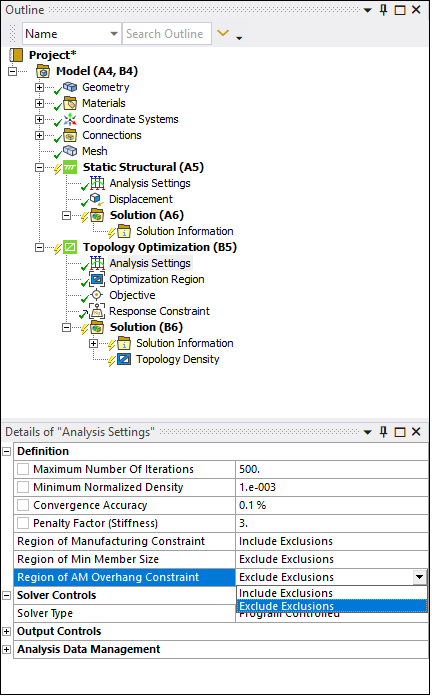
Density-Based Method
For the Density-Based method of Topology Optimization, a new Analysis Settings property is available, Region of AM Overhang Constraint, that enables you to include or exclude the Exclusions Region for creating self-supporting structures using the AM Overhang Constraint.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
Level Set Method
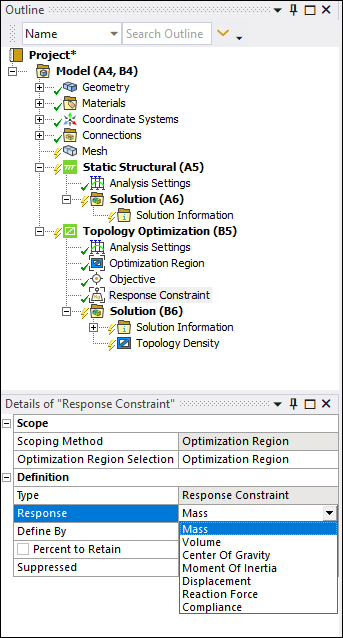
The Level Set Method for Topology Optimization analyses now enables you to specify multiple Optimization Region objects in order to optimize individual bodies with specific manufacturing constraints.
In addition, you can now specify the response types Center of Gravity and Moment of Inertia for geometric analyses and the Reaction Force constraint for static linear analyses.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
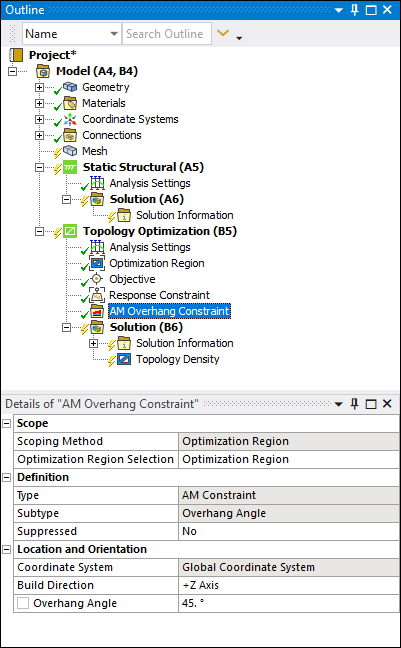
This method also now supports the AM Overhang Constraint, which enables you to specify Build Direction and Overhang Angle.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
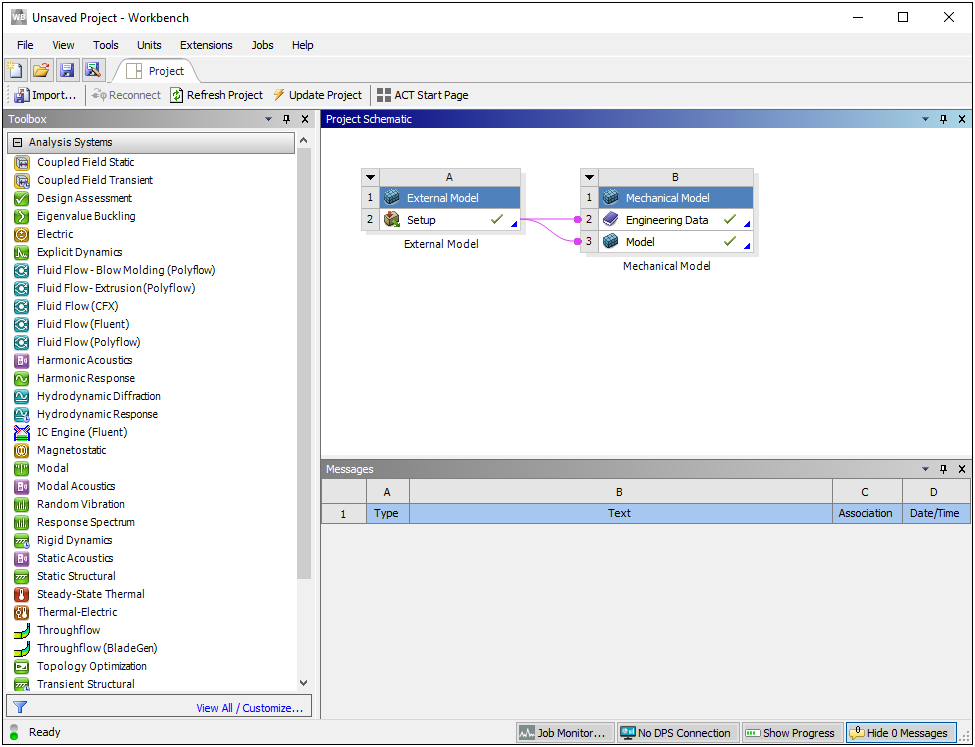
Importing a Mesh from within Mechanical
When you open the Mechanical application without importing a mesh, an Import option is available on the File Tab that enables you to import a mesh file from an External Model system. When you select the Import option, another new Mesh (External Model) option becomes available. This option opens a dialog that you use to select your mesh.
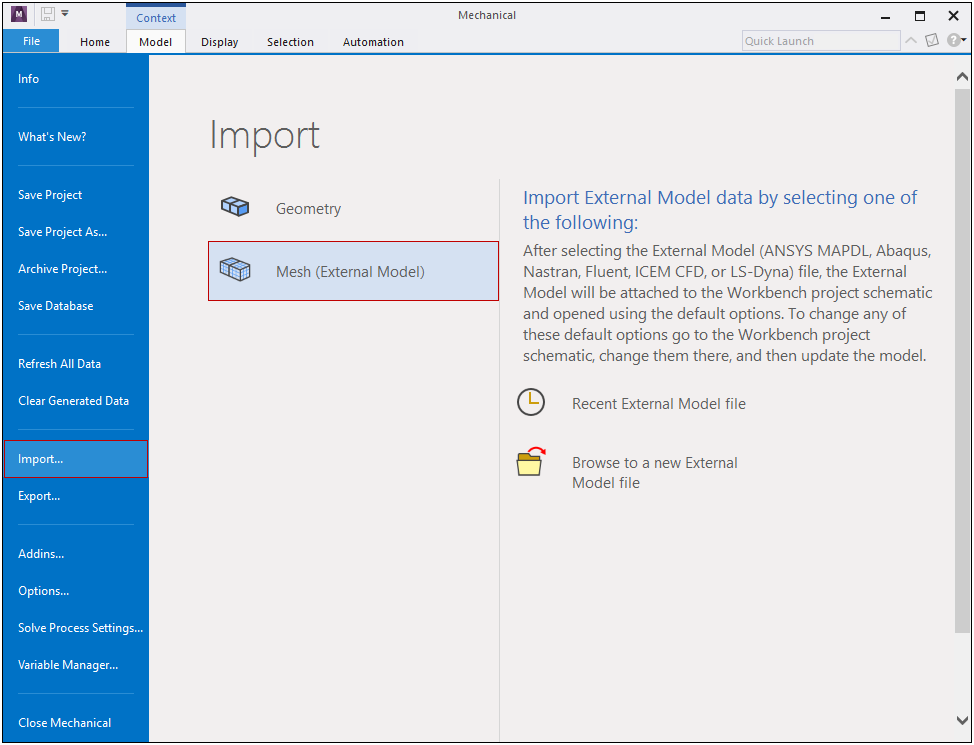
The application automatically creates and links the systems on the Project Schematic.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
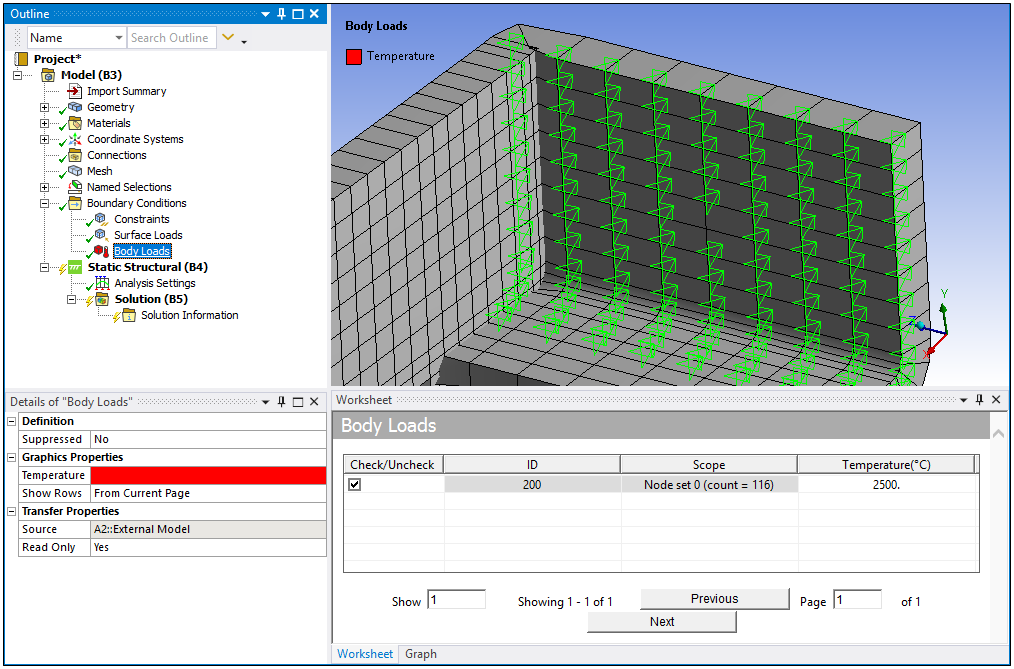
Nodal Body Force from Mechanical APDL Common Database Files
You can import the BF command from Mechanical APDL common database (.cdb) files.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
Import NASTRAN SPC Command as a Constraint
You can now import the SPC command for NASTRAN thermal analyses from NASTRAN Bulk Data (.bdf, .dat, .nas) files.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
Import ABAQUS Temperature-Dependent Plasticity
You can now transfer temperature dependency for the ABAQUS Commands *PLASTIC, with TYPE = ISOTROPIC, and *ELASTIC, with TYPE = ENGINEERING CONSTANTS, from the Engineering Data Workspace to Mechanical.
Fracture
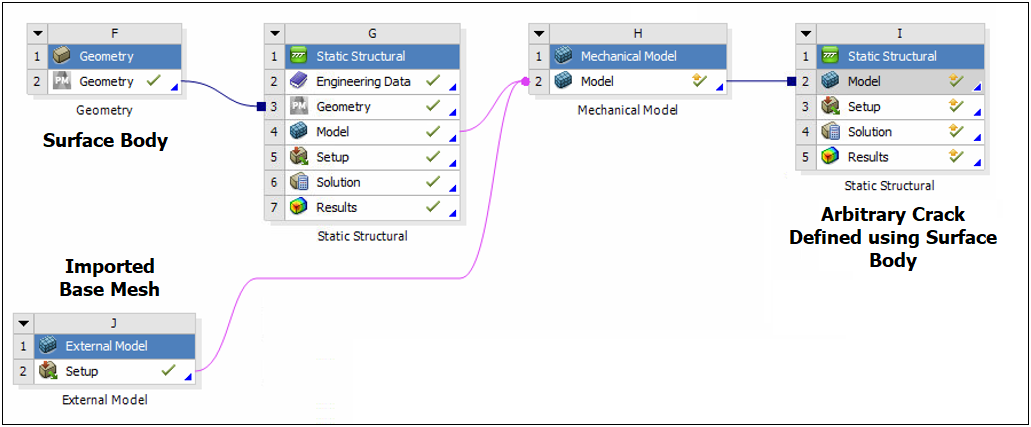
Arbitrary Crack on Imported Mesh from External Model
For a tetrahedron-based mesh that you import from External Model, you can now insert an Arbitrary Crack, generate an Arbitrary Crack mesh, and compute Fracture parameters associated with those cracks.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
Geometry and Connections
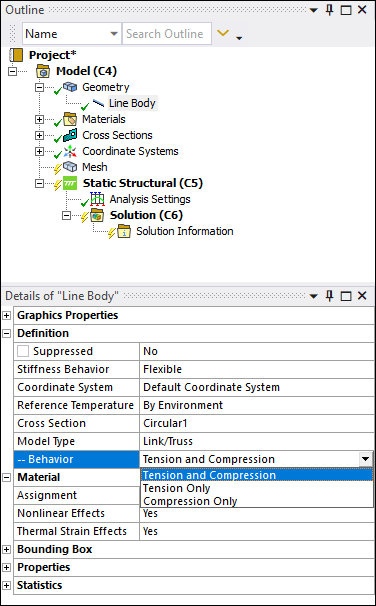
Compression/Tension for Line bodies
The Link/Truss option for the Model Type property for line bodies now supports the Behavior property. This enables you to specify tension and compression behavior using the property settings Tension and Compression (default), Tension Only, or Compression Only.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
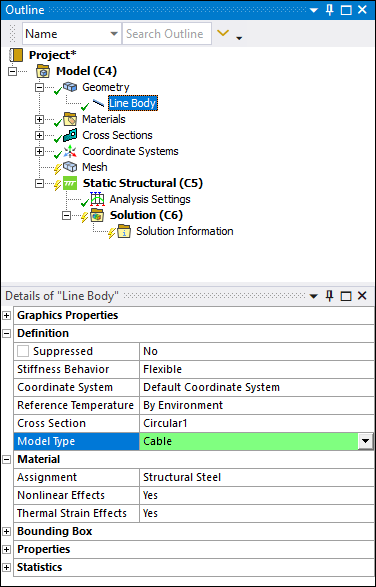
New Model Type for Line bodies
There is a new Model Type property for line bodies: Cable. This is a suitable option when analyzing uniaxial tension-only scenarios like cables. This option is equivalent to the Link/Truss option with the Behavior property set to Tension Only.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
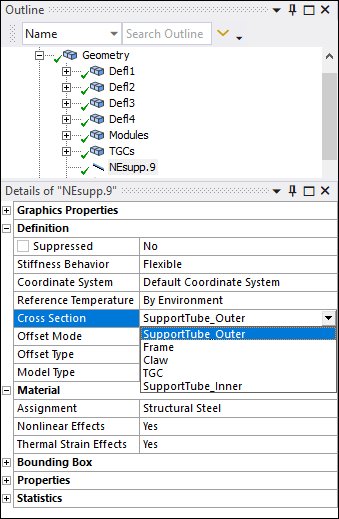
Changing Line Body Cross Sections
The Cross Section property is no longer read-only and enables you to make a selection from the available imported cross sections.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
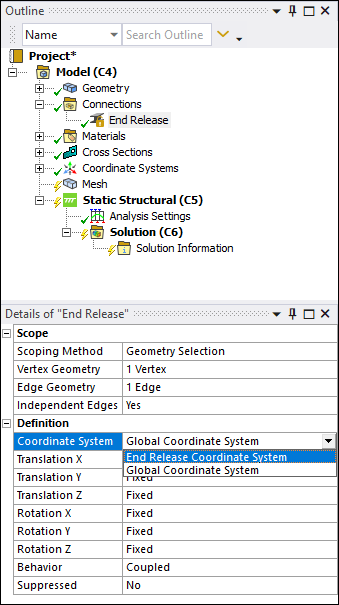
Beam Coordinate System for Beam End Release
The Coordinate System property for an End Release object now offer the option End Release Coordinate System. This option automatically creates an internal coordinate system that is not visible in the tree and that orients the End Release such that the x-axis is parallel to the scoped edge(s). This enables you to quickly define the orientation of the End Release when the specified Edge Geometry is not aligned with the Global Coordinate System.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
Mesh
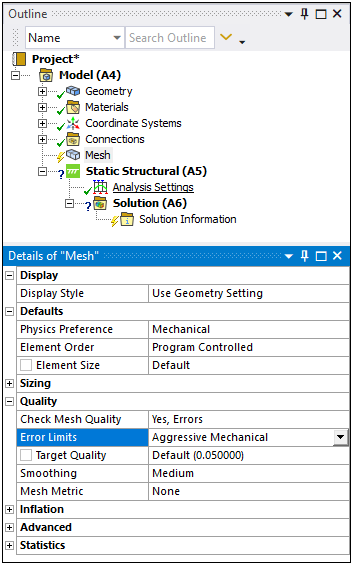
Aggressive Mechanical
In previous releases, the default setting for the Error Limits property was Standard Mechanical. The default setting is now Aggressive Mechanical. This sets stricter requirements for element quality that lead to better solution accuracy. If you experience long mesh processing times based on this new setting, or even a mesh failure, you can change the default setting in the Options dialog under the Meshing category.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
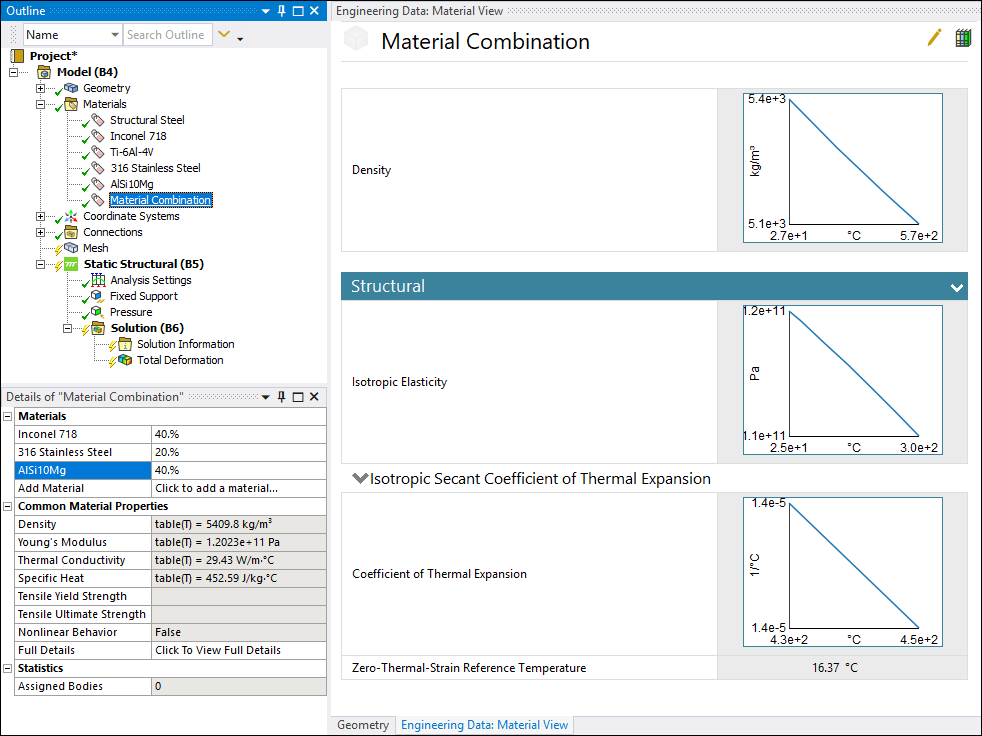
Materials Combination
A new Material Combination feature (object) enables you to combine materials based on supported specific material properties.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
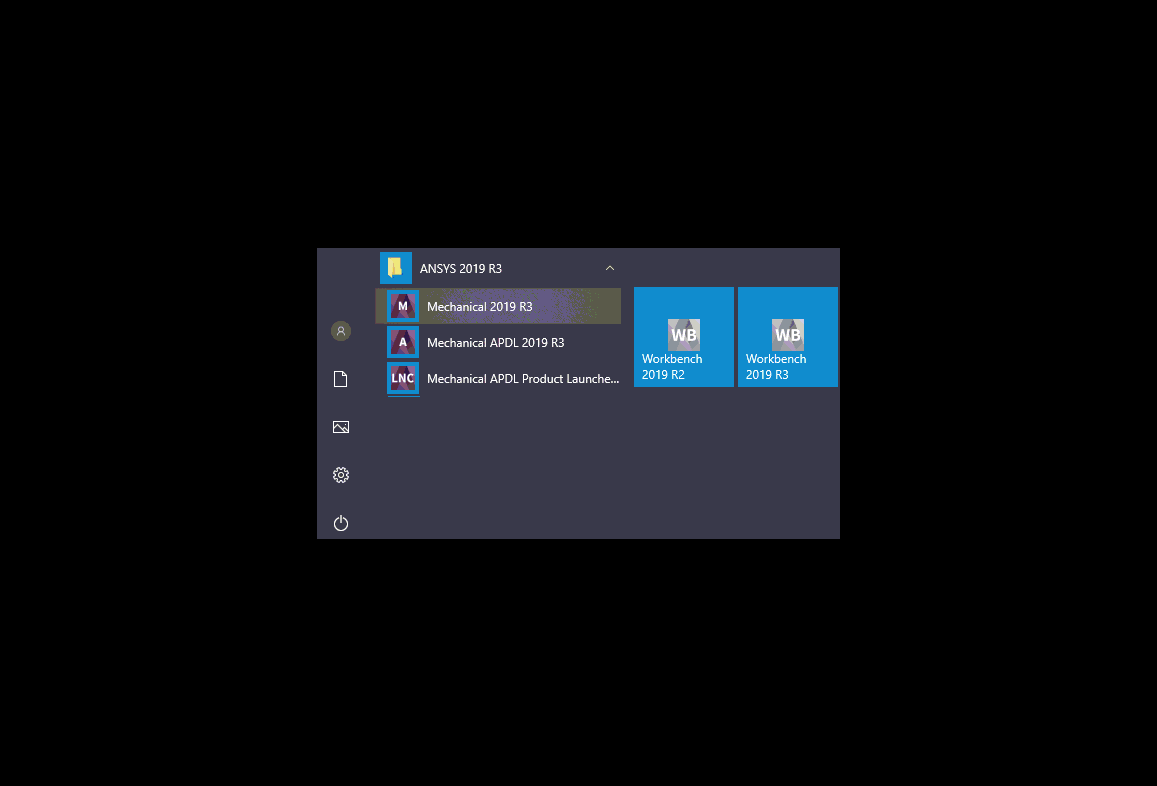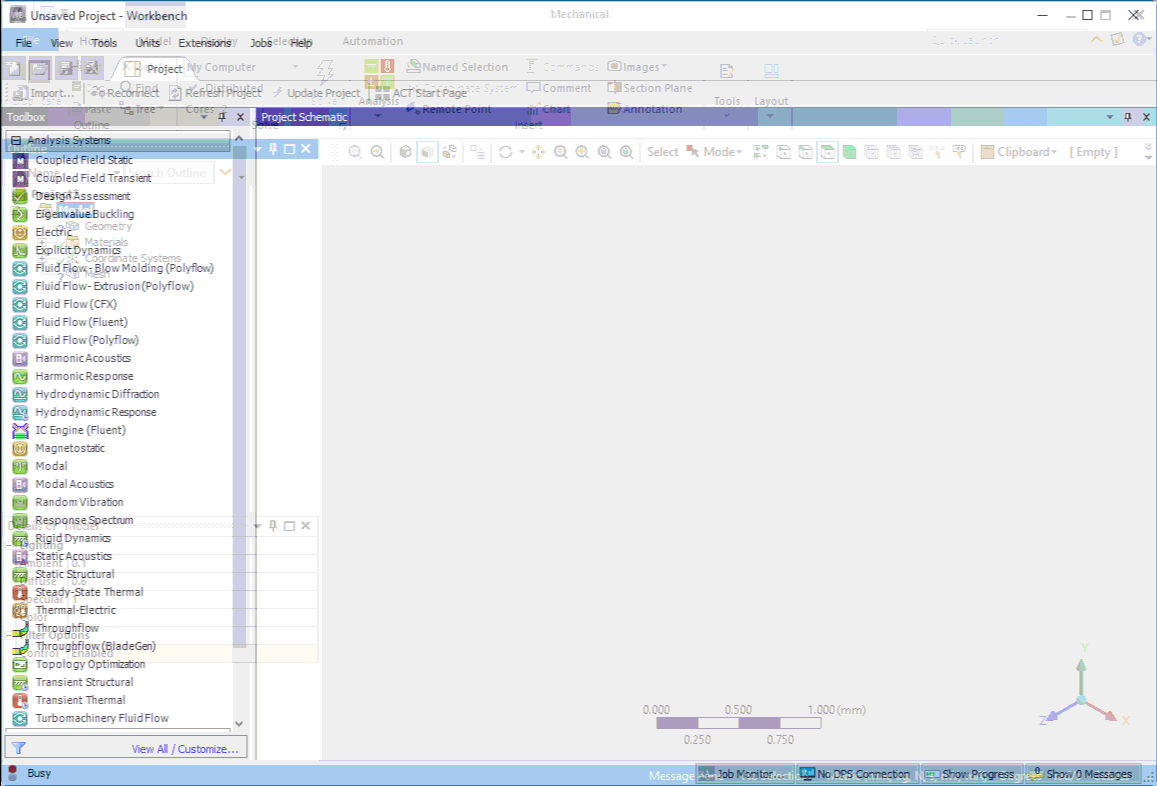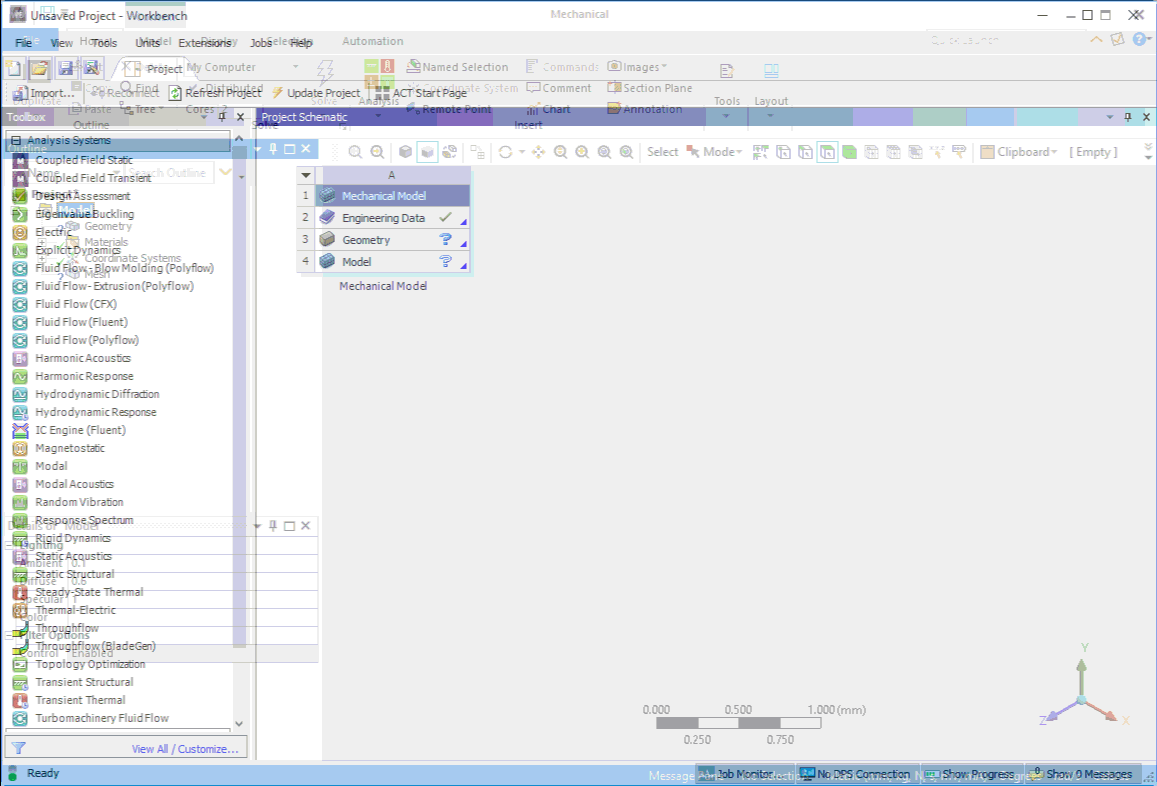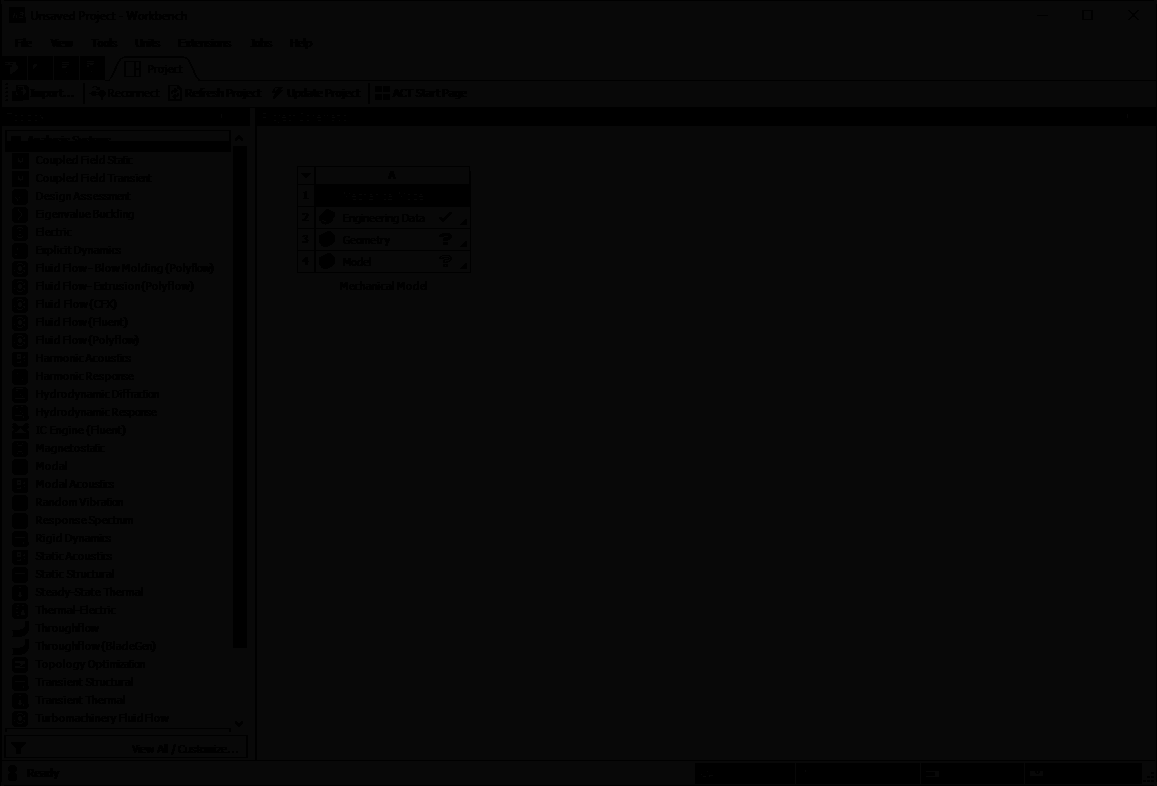
Launching Mechanical Directly from the Start Menu
Mechanical has a new ease-of-use option that enables you to open the application directly from the operating system Start menu. The ANSYS 2019 application menu provides the new option, Mechanical 2019 R3. This option opens Mechanical. The Workbench application also opens in the background and automatically inserts a Mechanical Model system into the Project Schematic.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
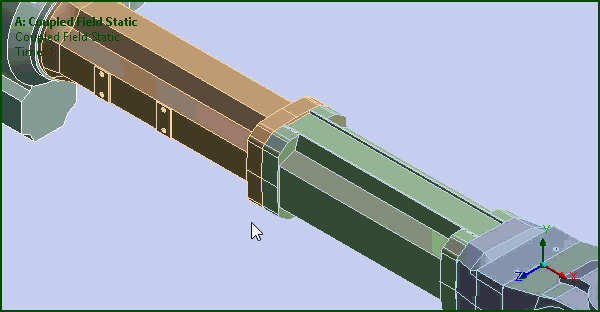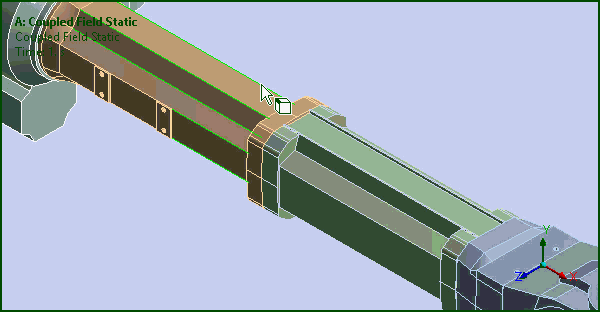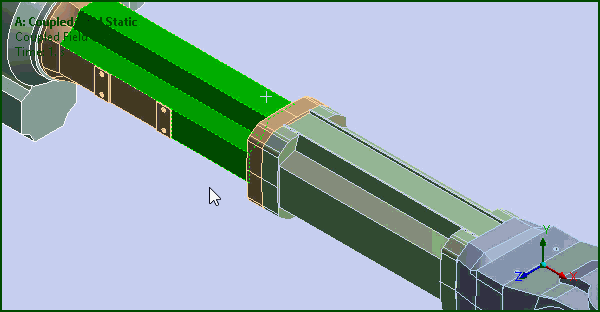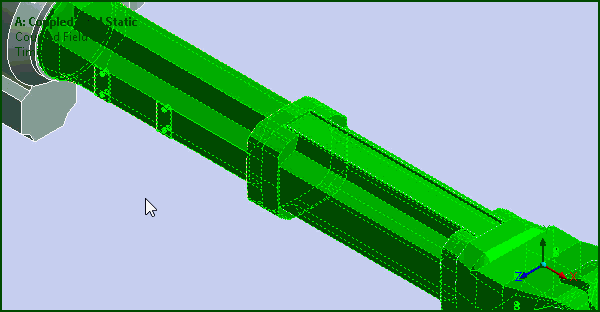
Smart Select
The Graphics Toolbar contains a new option: Smart Select. This selection filter enables you to select or highlight vertices, edges, and faces on the model without needing to specify a selection filter (Vertex, Edge, or Face) and supports multiple entity selection.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
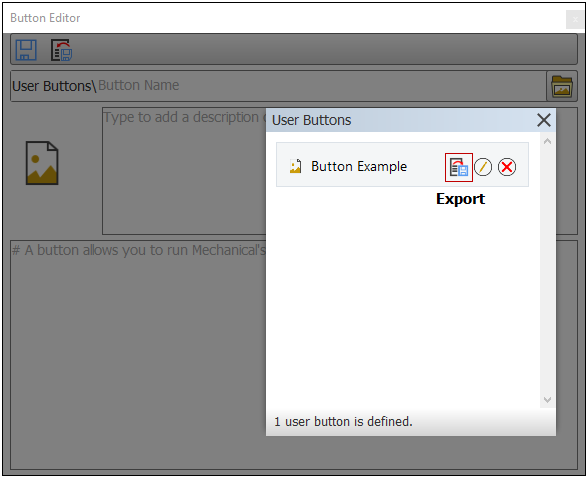
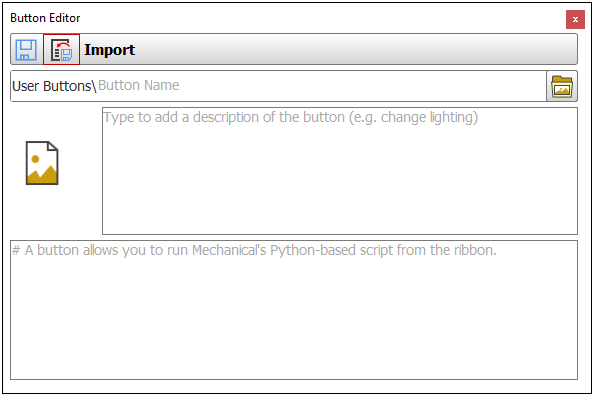
Exporting and Importing User-Defined Buttons
The feature to create unique toolbar buttons now has the ability to export your used-defined buttons. Once exported and saved, buttons can also be imported into the application.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
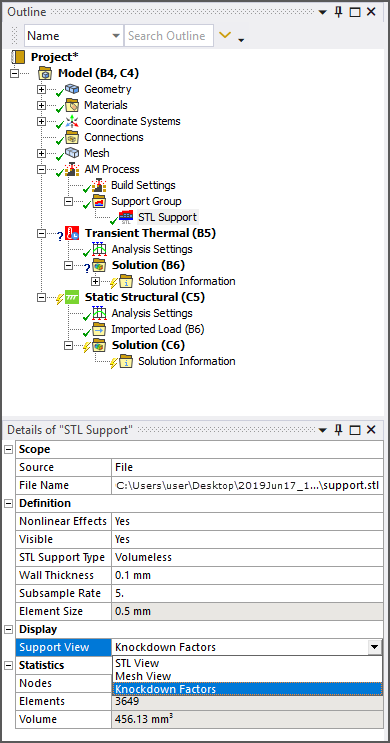
Viewing STL Supports
Supports inserted as STL Supports have a new display option that allows you to switch between viewing the STL supports, the mesh, or the knockdown factors. Knockdown factors are material multipliers that scale down the properties of elastic modulus, shear modulus, density, and thermal conductivity for the supports.
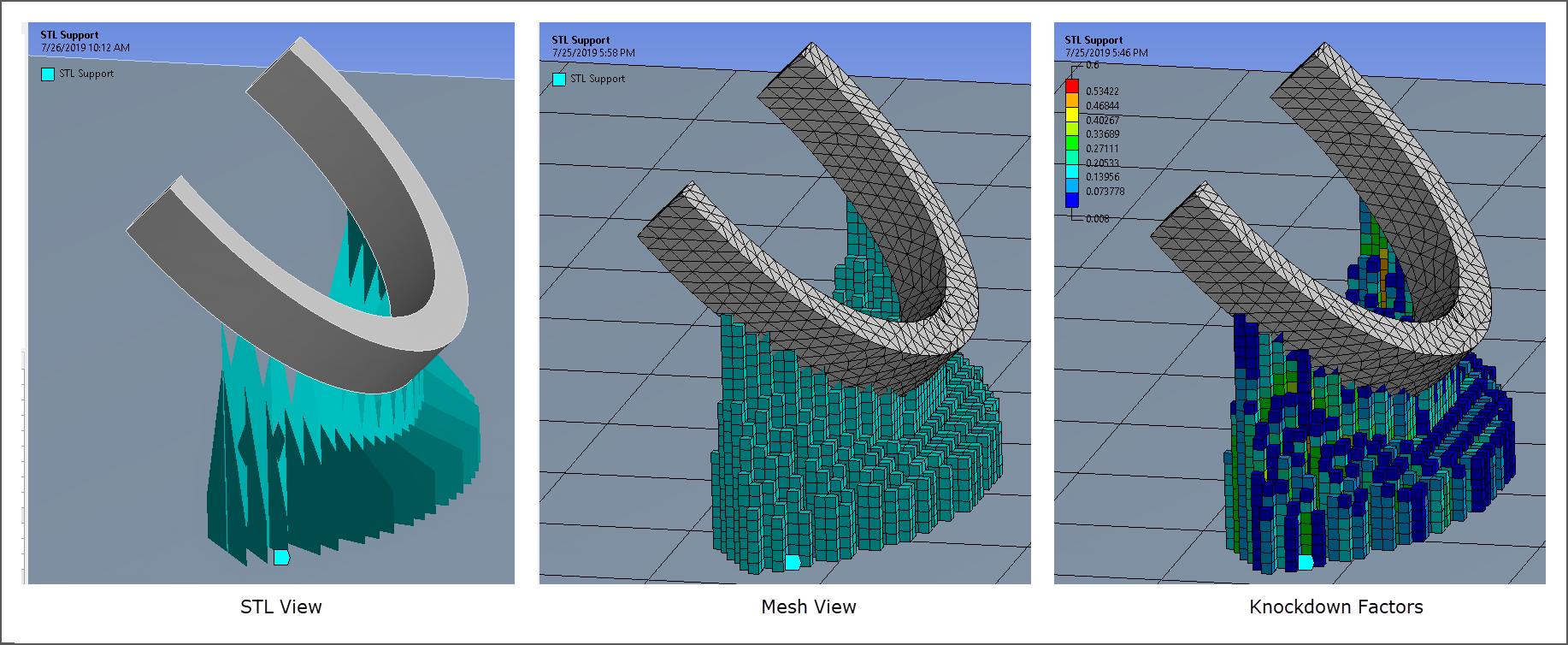
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
STL Support Removal
STL Supports may now be removed after cooldown using a removal step on the AM Process Sequencer.
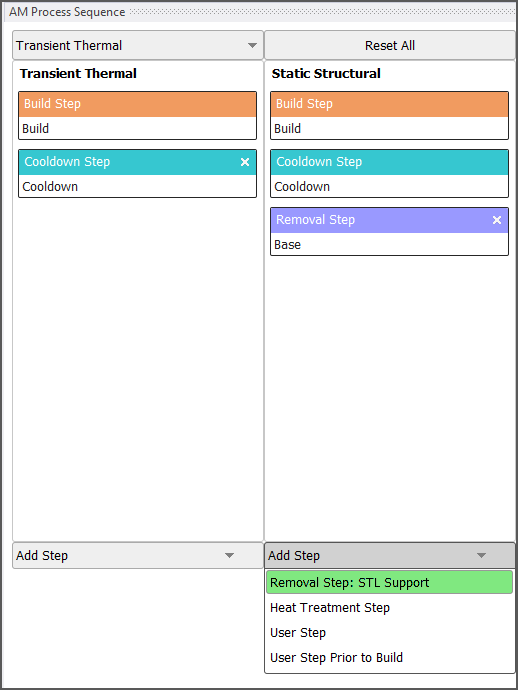
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
Line Bodies as Supports
When identifying predefined supports, line bodies may now be scoped, and they will be meshed with beam elements.
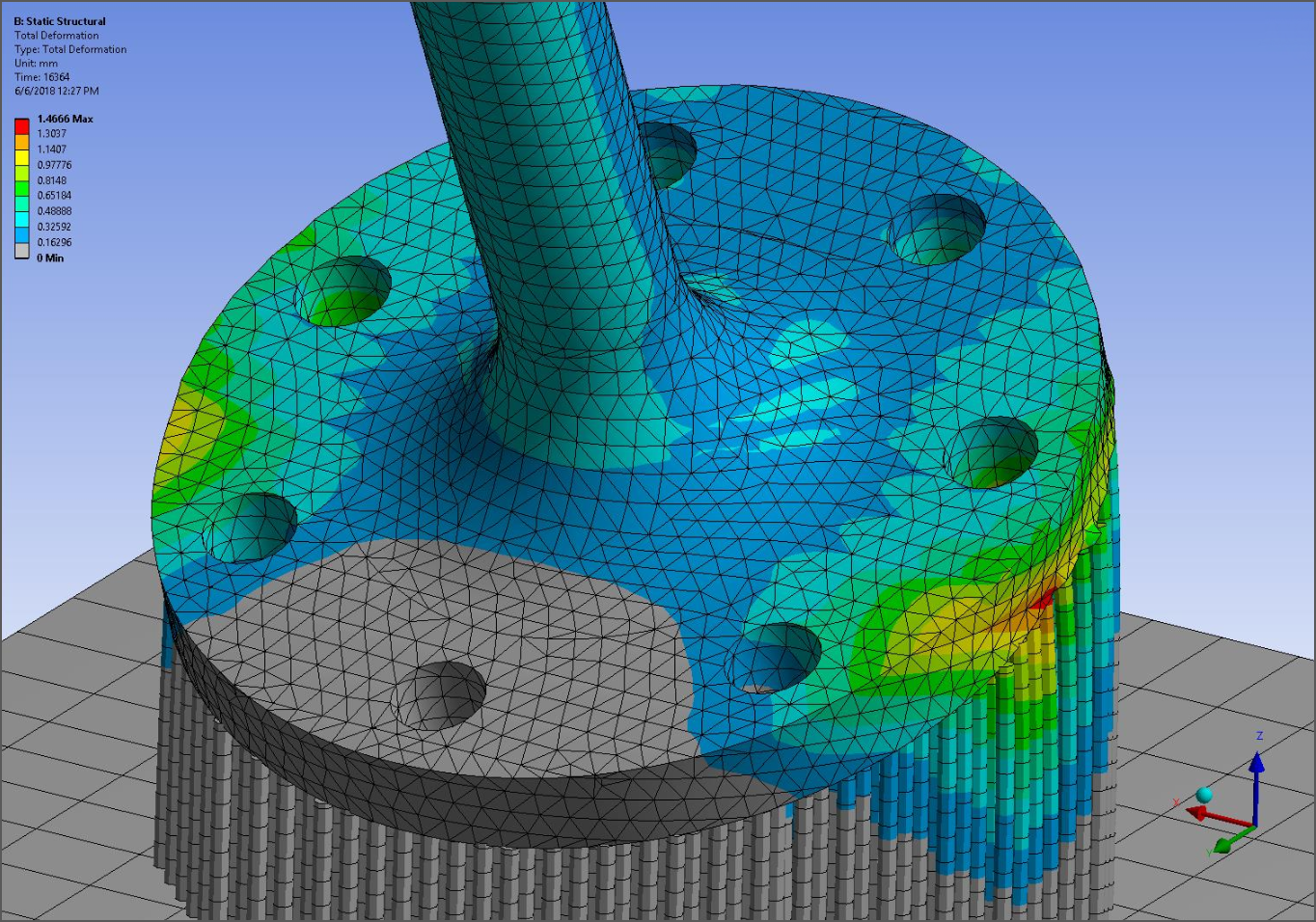
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
Identification of AM Process Steps in Results
AM process steps are now much more easily identifiable in the Graph window for result items under the Solution object.
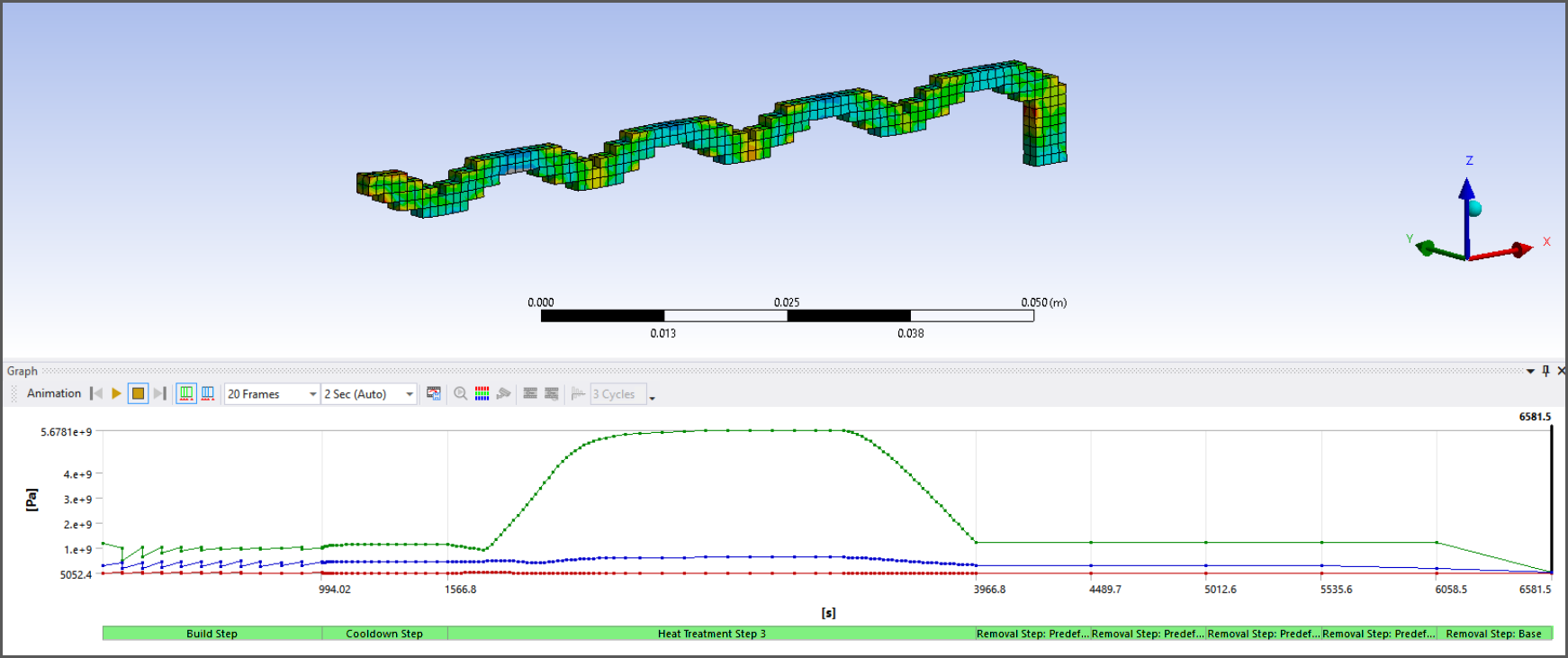
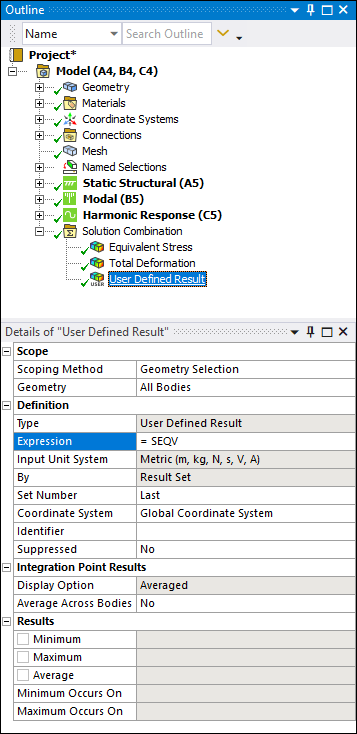
Solution Combination User-Defined Result Support
You can now incorporate User-Defined Results to query result file data when using the Solution Combination feature.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
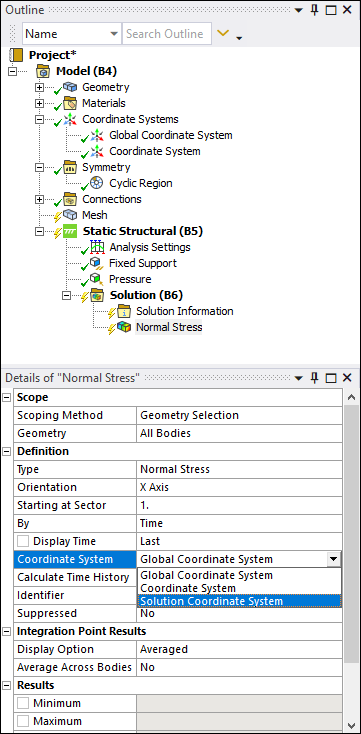
Cyclic Symmetry Result Specification
You can now specify supported result types with the Coordinate System option Solution Coordinate System.
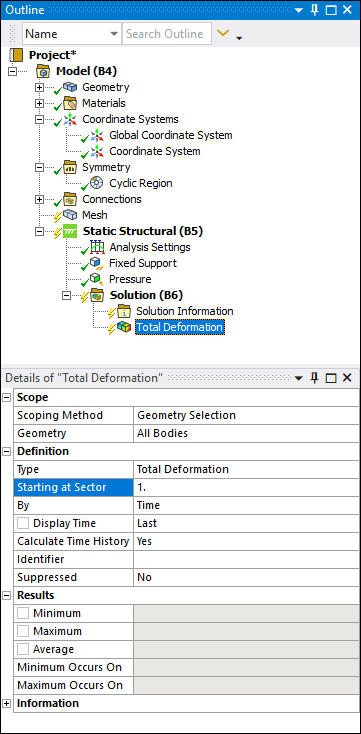
Result objects now contain a Starting at Sector property. This property gives you the ability to define different starting sectors for each result object.
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
Attached Camera (Rigid Body Analyses)
Attached Camera is a new option for the Animation feature. This option enables the animation of rigid bodies in such a way that the selected body is stationary and all other bodies move relative to, or about, the fixed body.
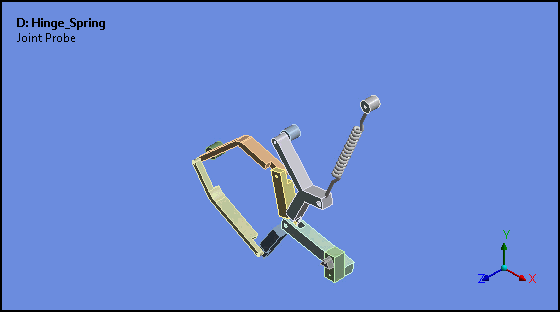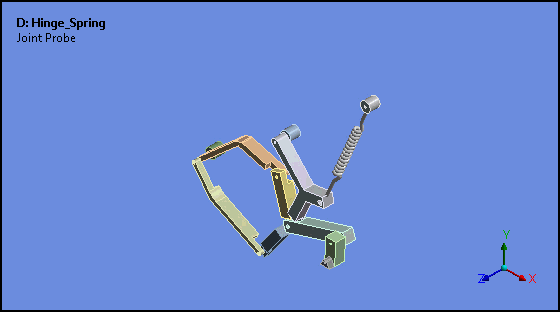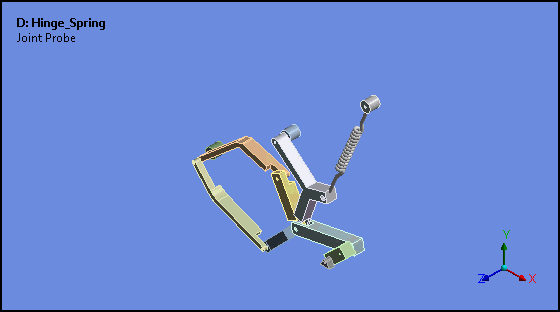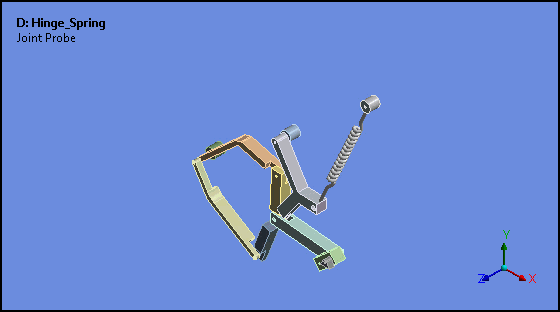
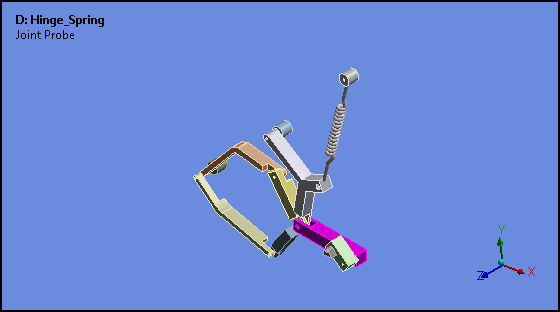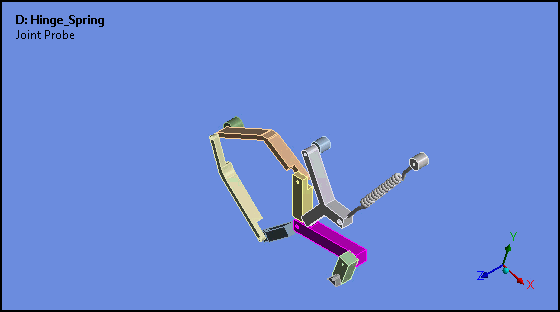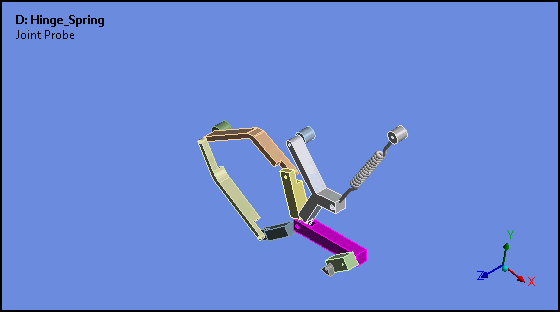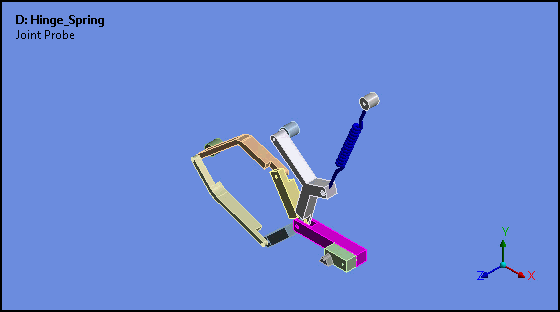
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
Exporting Acoustic Data as a .WAV File
For certain Acoustic analysis result types, you can now export the result in Waveform Audio File (.wav) format.
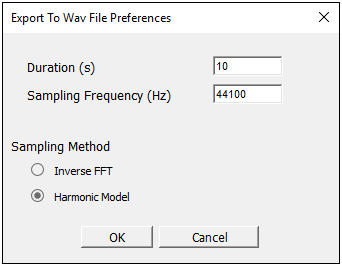
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
Hydrodynamic Pressure Mapping for Multiple Wave Cases
For a Static Structural analysis that is linked to a Hydrodynamic Diffraction analysis, the Wave Case Definition property of the Hydrodynamic Pressure load enables you to transfer pressures and loads for multiple wave frequency/direction pairs in a single calculation.
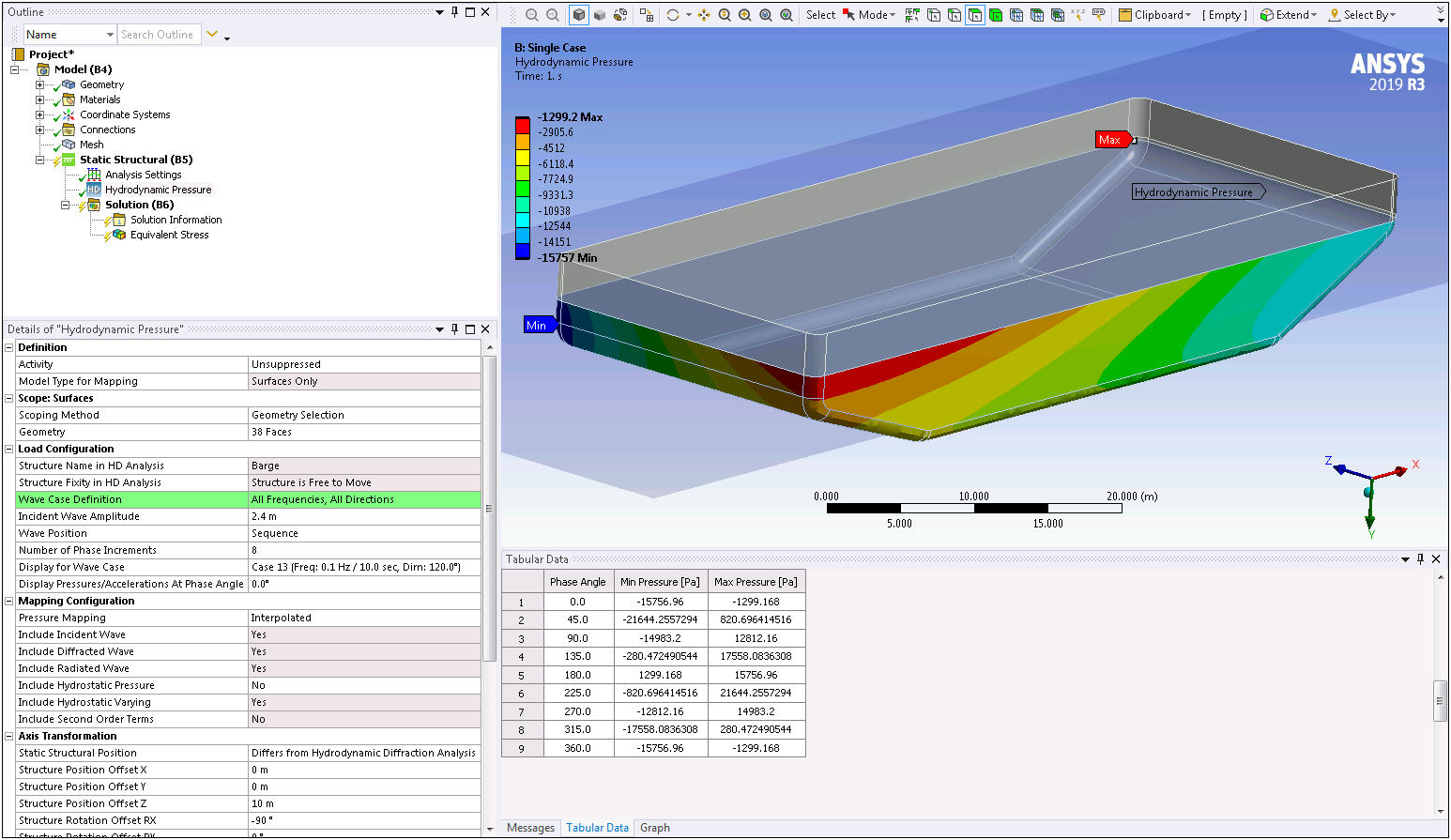
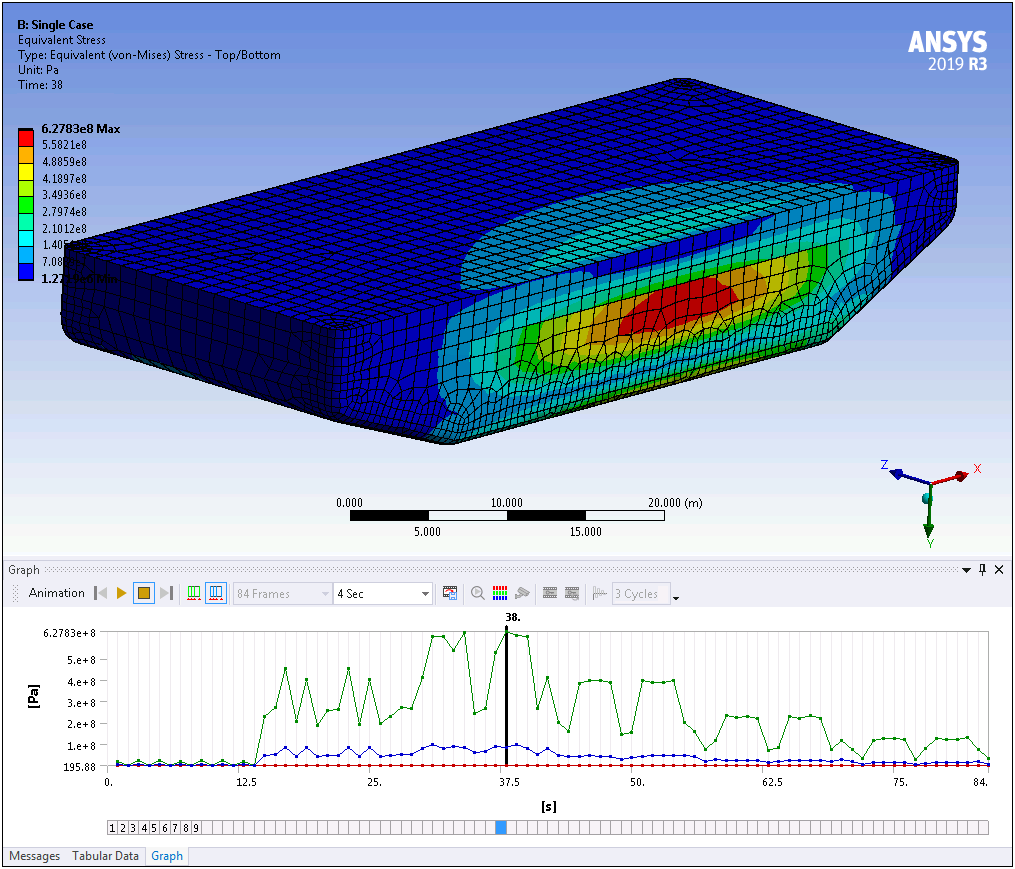
 Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
Want to learn
more? If you are on Windows, go to the documentation for this topic.
(Requires internet access
and will open in a new browser window. Not for Linux platforms.)
